June 2025
Courageous Core Model
May 2025
Five Phases of Change
April 2025
Frictionless Flow Framework
March 2025
Interaction Drivers
February 2025
Innovation Sins & Virtues
January 2025
Top Line Growth Pie
December 2024
Sustainability Maturity Ladder
November 2024
Self-Centered Thinking Traps
October 2024
Corporate Synergy Typology
September 2024
Guiding STAR Matrix
August 2024
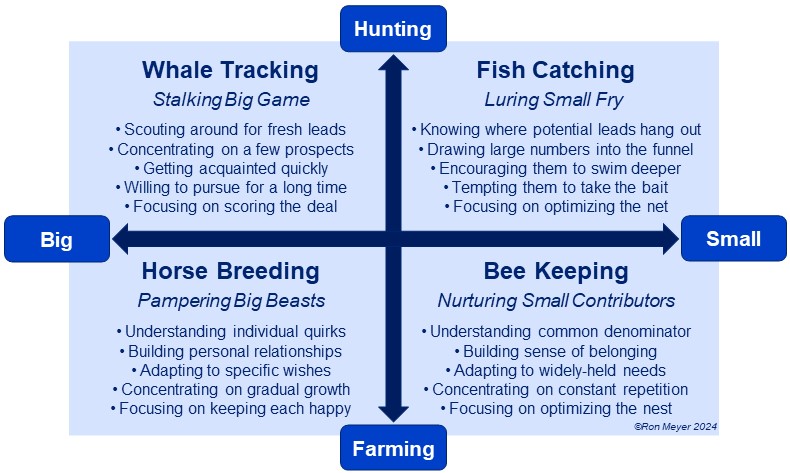
Hunting & Farming Typology
July 2024
Wicked Problem Scorecard
June 2024
Time Management Funnel
May 2024
Digitalization Staircase
April 2024
Leadership Circle Map
March 2024
MOVING Mission Framework
February 2024
BOLD Vision Framework
January 2024
Duty of Care Feedback Model
December 2023
Best Practice Sharing Modes
November 2023
Stakeholder Stance Map
October 2023
Status Snakes & Ladders
September 2023
Customer-Centricity Circle
August 2023
Activity System Dial
July 2023
New Pyramid Principle
June 2023
Cultural Fabric Model
May 2023
Corporate Strategy Framework
April 2023
Ambition Radar Screen
March 2023
Resistance to Change Typology
February 2023
5I Innovation Pipeline
January 2023
Thinking Directions Framework
December 2022
Corporate Management Styles
November 2022
Strategic Action Model
October 2022
Psychological Safety Compass
September 2022
The Tree of Power
August 2022
Value Proposition Dial
July 2022
Sustainable You Model
June 2022
Change Manager’s Toolbox
May 2022
Corporate Value Creation Model
April 2022
Organizational System Map
March 2022
Creativity X-Factor
February 2022
Strategic Alignment Model
January 2022
Market System Map
December 2021
Team Building Cycle
November 2021
Disciplined Dialogue Model
Oktober 2021
Strategy Hourglass
September 2021
Powerhouse Framework
August 2021
Fruits & Nuts Matrix
July 2021
Everest Model of Change
June 2021
Followership Cycle
May 2021
Knowledge Sharing Bridges
April 2021
Innovation Box
March 2021
Empowerment Cycle
February 2021
Digital Distribution Model Dial
January 2021
Digital Product Model Dial
December 2020
4C Leadership Levers
November 2020
Rebound Model of Resilience
October 2020
Strategic Bets Framework
September 2020
Storytelling Scripts
August 2020
7I Roles of the Corporate Center
July 2020
Strategy Development Cycle
June 2020
Rising Star Framework
May 2020
The Control Panel
April 2020
Strategic Agility Model
March 2020
Leadership Fairness Framework
February 2020
11C Synergy Model
January 2020
Competition Tornado
December 2019
Confidence Quotient
November 2019
House of Engagement
October 2019
Revenue Model Framework
September 2019
Interaction Pressure Gauge
August 2019
Digital Platform Map
July 2019
Mind the Gap Model